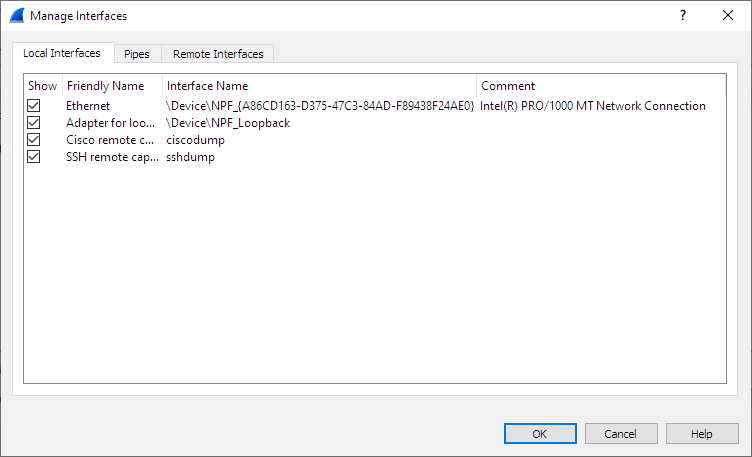
The “Manage Interfaces” dialog box initially shows the “Local Interfaces” tab, which lets you manage the following:
- Show
- Whether or not to show or hide this interface in the welcome screen and the “Capture Options” dialog.
- Friendly Name
- A name for the interface that is human readable.
- Interface Name
- The device name of the interface.
- Comment
- Can be used to add a descriptive comment for the interface.
The “Pipes” tab lets you capture from a named pipe. To successfully add a pipe, its associated named pipe must have already been created. Click and type the name of the pipe including its path. Alternatively, can be used to locate the pipe.
To remove a pipe from the list of interfaces, select it and press .
On Microsoft Windows, the “Remote Interfaces” tab lets you capture from an interface on a different machine. The Remote Packet Capture Protocol service must first be running on the target platform before Wireshark can connect to it. The easiest way is to install Npcap from {npcap-download-url} on the target. Once installation is completed go to the Services control panel, find the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service and start it.
On Linux or Unix you can capture (and do so more securely) through an SSH tunnel.
To add a new remote capture interface, click and specify the following:
- Host
- The IP address or host name of the target platform where the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service is listening. The drop down list contains the hosts that have previously been successfully contacted. The list can be emptied by choosing “Clear list” from the drop down list.
- Port
- Set the port number where the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service is listening on. Leave blank to use the default port (2002).
- Null authentication
- Select this if you don’t need authentication to take place for a remote capture to be started. This depends on the target platform. This is exactly as secure as it appears, i.e. it is not secure at all.
- Password authentication
- Lets you specify the username and password required to connect to the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service.
Each interface can optionally be hidden.
In contrast to the local interfaces they are not saved in the preferences file.
| Note | |
|---|---|
|
Make sure you have outside access to port 2002 on the target platform. This is the default port used by the Remote Packet Capture Protocol service. |
To remove a host including all its interfaces from the list, select it and click the button.